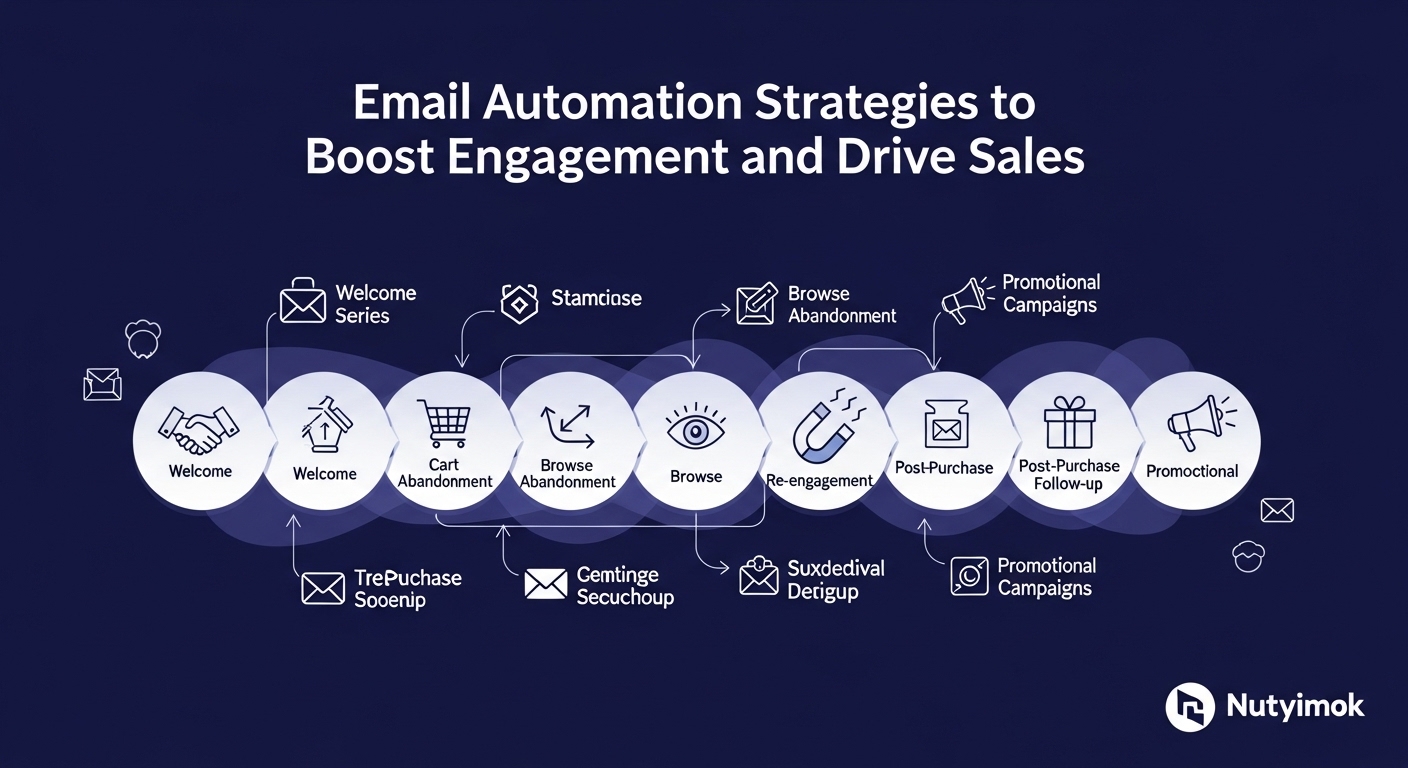
Understanding Email Automation
Email automation refers to the use of software to send emails automatically based on pre-defined triggers and personalized parameters. This strategy allows businesses to deliver timely, relevant content to their audience with minimal manual effort, making it a key component for enhancing engagement and driving sales.
The Importance of Segmentation
Segmentation is crucial for effective email marketing. By dividing your audience into smaller groups based on demographics, behavior, or preferences, you can tailor your messaging to be more relevant. Consider the following segmentation strategies:
-
Demographic Segmentation: Categorize your audience based on age, gender, job title, and location. This allows for personalized content that resonates with specific groups.
-
Behavioral Segmentation: Monitor user behavior, such as past purchases, website activity, and email engagement. Use this data to send targeted offers that drive conversions.
-
Lifecycle Segmentation: Segment contacts based on their stage in the buyer’s journey—new subscribers, active customers, and lapsed customers require different messaging to maximize engagement.
- Preference-Based Segmentation: Allow users to set preferences for content types they are interested in receiving, which can drastically improve open rates and engagement scores.
Crafting Personalized Content
Personalization extends beyond inserting a recipient’s name in an email. Consider these techniques:
-
Dynamic Content: Use tools that allow you to customize portions of your emails based on recipient data, interests, or behaviors.
-
Recommendations Engine: Implement algorithms that suggest products based on past purchases and browsing history.
- Tailored Subject Lines: Experiment with subject lines that reflect the recipient’s interests or recent activities, increasing open rates.
Utilizing Triggered Emails
Triggered emails are automated messages sent in response to customer actions, significantly improving engagement. Here are some effective triggered email types:
-
Welcome Series: Send a series of onboarding emails that introduce your company, outline what to expect, and provide exclusive offers.
-
Abandoned Cart Emails: Remind customers of items they left behind in their shopping cart to recapture lost sales.
-
Follow-up Emails: After purchases, send follow-up emails requesting feedback, offering product suggestions, or providing care tips to keep customers engaged.
- Renewal Reminders: For subscription services, automate reminders for renewals or upgrades, ensuring your customers remain informed and engaged with your brand.
A/B Testing for Optimization
A/B testing involves comparing two versions of an email to determine which performs better. Test various elements of your campaigns:
-
Subject Lines: Experiment with different lengths, tones, and calls to action to learn what captivates your audience’s attention.
-
Visual Layouts: Compare single-column vs. multi-column layouts to assess which style resonates more with your audience.
- Call to Action (CTA): Test different wording, colors, and placements for your CTAs to find the combination that generates the highest click-through rates.
Timing and Frequency
The timing and frequency of your emails can significantly impact engagement rates. Consider the following strategies:
-
Optimal Send Times: Analyze your audience’s behaviors to determine when they are most likely to open emails. Generally, mid-morning and mid-afternoon on weekdays tend to yield high engagement.
- Frequency: Avoid overwhelming your audience with too many emails. Establish a consistent rhythm that keeps your brand top-of-mind without becoming bothersome. Test different frequencies to find the sweet spot through analytics.
Engaging Design Elements
The design of your emails plays a crucial role in retaining attention. Focus on the following elements:
-
Responsive Design: Ensure your emails are mobile-friendly since a significant percentage of users check emails on their mobile devices.
-
Visual Hierarchy: Use headings, images, and bullet points to create a visual hierarchy that guides the reader through your content effectively.
- Clear CTAs: Make your calls to action stand out through contrasting colors and strategic positioning within the email to encourage clicks.
Analytics and Improvement
The success of email automation lies in analyzing metrics. Focus on these key performance indicators (KPIs):
-
Open Rate: Measures the percentage of recipients who opened the email, providing insights into subject line effectiveness.
-
Click-Through Rate (CTR): Evaluates how many recipients clicked on links within the email, indicating engagement level with the content.
-
Conversion Rate: Tracks how many recipients completed desired actions, such as making a purchase, giving insight into campaign effectiveness.
- Unsubscribe Rate: Monitor how many users opt-out of your emails to understand audience satisfaction and content relevancy.
Tools for Email Automation
Consider investing in robust email automation platforms such as:
-
Mailchimp: Offers user-friendly design tools, segmentation features, and advanced analytics.
-
HubSpot: Known for its comprehensive marketing suite, it includes powerful automation workflows and CRM integration.
- ActiveCampaign: Provides advanced automation and segmentation capabilities catered to deliver highly targeted campaigns.
Compliance and Best Practices
Ensure your campaigns are compliant with legal regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the CAN-SPAM Act. Always include:
-
Easy opt-out options: Respect user preferences by allowing easy unsubscriptions.
- Clear privacy policy: Inform users about data collection practices to build trust.
By employing a combination of advanced segmentation, personalized content, triggered emails, and rigorous testing, businesses can leverage email automation effectively to engage their audience and drive sales. Each of these strategies works synergistically, allowing brands to maintain a meaningful dialogue with customers while delivering tailored content that resonates and compels action.