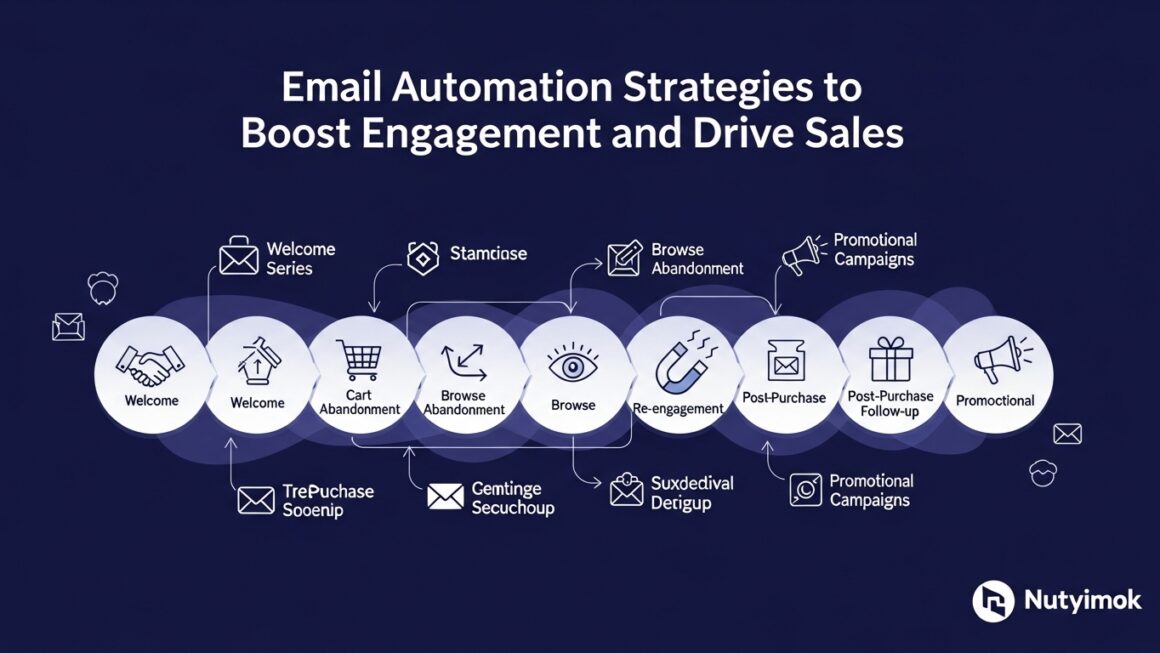
Understanding Automation Strategy: A Comprehensive Definition
What is Automation Strategy?
Automation strategy refers to the structured approach an organization develops to integrate automation into its operations and processes. It is a comprehensive plan that outlines how to utilize technology and automation tools to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance productivity. The strategy encompasses the selection of tools, the systems to automate, prioritization, implementation process, and continuous assessment.
Key Components of an Automation Strategy
-
Assessment of Current Processes
Understanding which processes are most suitable for automation is crucial. This involves identifying repetitive, time-consuming tasks, and evaluating existing workflows to determine inefficiencies. Organizations typically conduct process mapping or analysis to pinpoint key areas for improvement. These assessments often incorporate employee feedback and performance metrics to understand the pain points better. -
Defining Objectives
Clear objectives are vital for establishing direction. Organizations must define what they aim to achieve with automation—whether it’s cost savings, improved accuracy, enhanced speed, or employee satisfaction. Setting specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals helps focus automation efforts and serves as a benchmark for success. -
Selecting Automation Tools and Technologies
The automation landscape is vast, offering various tools and technologies, from robotic process automation (RPA) to artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. The selected tools should align with organizational goals and the processes identified for automation. Factors such as ease of integration, scalability, and user-friendliness should guide tool selection. -
Change Management
Successfully implementing an automation strategy often requires culture change within the organization. Employees may feel threatened by automation, leading to resistance. Adequate training and communication are essential. Creating a change management plan that fosters a culture of innovation and embraces new technologies can ease this transition. -
Implementation Plan
An effective implementation plan details the roadmap for automation execution. This plan should include timelines, resources needed, and roles and responsibilities. Pilot projects can help identify potential challenges and demonstrate the operational impact of automation before a full rollout. - Monitoring and Optimization
Post-implementation, it’s crucial to continuously monitor automated processes to ensure they meet the defined objectives. Key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics should be established beforehand to assess effectiveness. Regular evaluations enable organizations to identify areas for further optimization and refinement.
Challenges in Crafting an Automation Strategy
-
Integration Complexity
Integrating automation tools with existing systems can be complex. Systems often have varying compatibilities, which can cause disruptions. A successful strategy will consider the potential technical challenges and develop solutions for seamless integration. -
Skill Gaps
The adoption of automation tools may require specific technical skills or knowledge that current staff may lack. Organizations must recognize these skill gaps and invest in training or hiring new talent to ensure a successful implementation. Continuous education should be part of the strategy. - Data Management
Automation relies heavily on data. Inaccurate or poorly managed data can undermine automation efforts. A robust data management strategy should be part of an automation strategy, ensuring that data input is accurate and up to date.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Automation Strategy
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a cornerstone of modern automation strategies. AI enhances the capabilities of traditional automation by enabling systems to learn from data, adapt to changes, and make decisions. Integration of AI tools can lead to more complex automation applications, such as predictive analytics and customer service chatbots.
-
Enhanced Decision-Making
AI enables automation systems to analyze vast datasets in real-time, enabling informed decision-making. This facilitates proactive management instead of reactive solutions. -
Process Personalization
In customer service, AI automates interactions while personalizing the experience based on user data. Such tailored responses can improve customer satisfaction and loyalty. - Predictive Maintenance
For manufacturing and logistics, AI-driven automation can predict equipment failures by analyzing historical data patterns, significantly reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
Measuring Success in Automation Strategy
Establishing success metrics is paramount in tracking the effectiveness of an automation strategy. Organizations should evaluate both quantitative and qualitative metrics, which may include:
-
Cost Reduction
Monitoring savings in operational costs is fundamental. A successful strategy will often show measurable reductions in labor costs and operational expenditures. -
Increased Efficiency
Automation should streamline processes, thereby increasing overall efficiency. Metrics like time saved per task and throughput rates can quantitatively assess this aspect. -
Employee Engagement
Automation can impact employee satisfaction levels. Surveys and feedback should be collected post-implementation to understand employee sentiment about their workload and roles. - Customer Satisfaction
Customer feedback and service levels can also indicate the success of implemented automation processes. Improvements in response times and service quality are key indicators.
Future Trends in Automation Strategy
-
Hyperautomation
As organizations seek more advanced automation solutions, hyperautomation—a combination of multiple automation tools—will become increasingly prevalent. This approach enables comprehensive end-to-end automation across business processes. -
Integration of IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) will enhance automation strategies by enabling devices to communicate and exchange data seamlessly, leading to smarter data-driven automation processes. -
Focus on Cybersecurity
As automation increases, so does the need for security measures. Organizations will need to integrate robust cybersecurity protocols to protect automated systems from potential threats. -
Sustainable Automation
Environmental considerations will drive the adoption of automation strategies that prioritize sustainability. Businesses will increasingly explore automation solutions that reduce waste and energy consumption. - Collaborative Automation
The future will likely see greater collaboration between humans and machines, where automation assists employees rather than replacing them. This co-existence can enhance productivity and creativity in the workforce.
By understanding these elements, businesses can create an effective automation strategy tailored to their unique needs, ensuring a competitive edge in the modern marketplace. Each component plays an integral role in shaping how organizations leverage automation effectively, ultimately transforming operations for sustained success.